Zirconium alloys are solid solutions of zirconium or other metals.
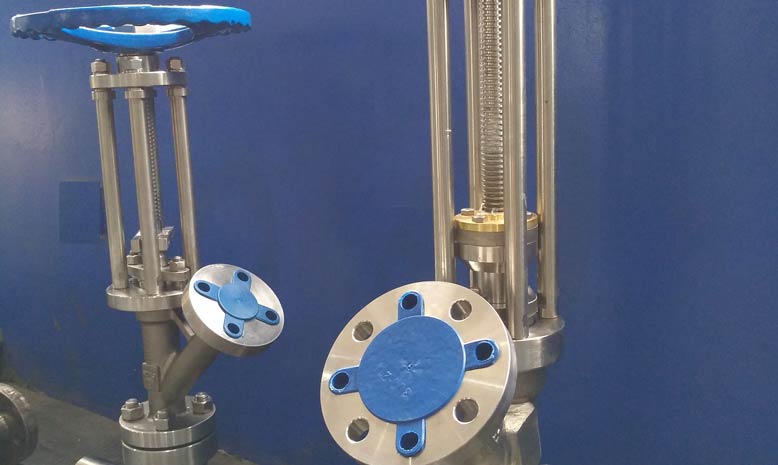

Zirconium has a very low thermal neutron absorption cross-section, high hardness, ductility, and corrosion resistance. The main use of zirconium alloys is in nuclear technology, such as fuel rods in nuclear reactors. Nuclear-grade zirconium alloys typically consist of more than 95% zirconium and less than 2% tin, niobium, iron, chromium, nickel, and other metals, which are added to improve mechanical properties and corrosion resistance.
Have excellent corrosion resistance for any density and high temperature even boiling hydrochloric acid, it is not easy to have slit corrosion, point corrosion, and stress corrosion.
Available in the sulfuric acid medium which a density below 70% and temperature is a boiling point or higher than the boiling point.
Available in any density acetic acid medium below 250℃, and does not corrode nearly.
It is a unique anti-corrosion material that applicable for any density alkaline solution and the fusing alkali medium.
It has extremely good corrosion resistance in organic acid.
Forbid strictly applying in the hydrofluoric acid, the aqua regia, the hydrofluosilicic acid, and sulfuric acid, in the nitric acid nitration mixture medium.
Forbid strictly using in the dry chlorine and the fuming Nitric acid medium.
Must fully consider the corrosive medium temperature, medium ingredient, various ingredients density, water content, and so on four aspects when selecting the zirconium valves.
Design Features
Desgin: HG5-89-1 &HG-16-79
Flanged Ends: ASME B16.5 RF
Test: ASME 598
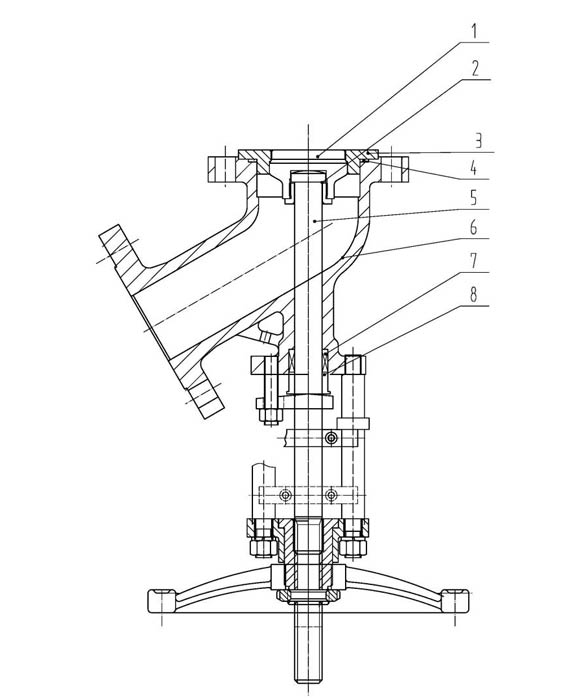
Parts & Material
No. | Part Name | Material |
1 | Disc | Zirconium |
2 | Disc bonnet | Zirconium |
3 | Seat | Zirconium |
4 | Gasket | Zirconium+Graphite |
5 | Stem | Zirconium |
6 | Body | Zirconium |
7 | Packing | Graphite |
8 | Gland bushing | Zirconium |